 Black Box Testing Techniques: Use Case Testing
Black Box Testing Techniques: Use Case Testing
In previous articles we learned about Testing Techniques Overview and then Specification Based Testing Techniques or Black Box testing t...
 Black Box Testing Techniques: Use Case Testing
Black Box Testing Techniques: Use Case Testing
In previous articles we learned about Testing Techniques Overview and then Specification Based Testing Techniques or Black Box testing t...
 Black Box Testing Techniques : State Transition Testing
Black Box Testing Techniques : State Transition Testing
In previous articles we learned about Testing Techniques Overview and then Specification Based Testing Techniques or Black Box testing t...
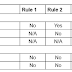 Black Box Testing Techniques : Decision Table Testing
Black Box Testing Techniques : Decision Table Testing
In previous articles we learned about Testing Techniques Overview and then Specification Based Testing Techniques or Black Box testing te...
 Common terms used in mobile application development and testing
Common terms used in mobile application development and testing
Android application package file (APK) – a file format that is used deliver mobile apps to Android devices App builds – a process of comp...
 Complete Tutorial on Mobile apps testing- Learn how to perform mobile apps testing stey by step guide
Complete Tutorial on Mobile apps testing- Learn how to perform mobile apps testing stey by step guide
Mobile application testing is a process by which application software developed for hand held mobile devices is tested for its function...